In our conventional wisdom, it seems that only the elderly are troubled by bone diseases. Indeed, aging increases the chances of developing these diseases, but statistics show that bone diseases such as osteoporosis and osteoarthritis are showing a trend of affecting younger people. For example, there are more than 130 million osteoarthritis patients in my country, of whom about one-third are young and middle-aged people.
Bones and joints age much earlier than we imagine. To prevent them from developing into serious diseases prematurely, it’s essential to take care of them by consuming plenty of nutrients beneficial to bone health. Collagen peptides, as small-molecule, easily absorbed active nutrients, have been thoroughly proven to comprehensively promote bone health and possess powerful effects in nourishing and repairing bones.
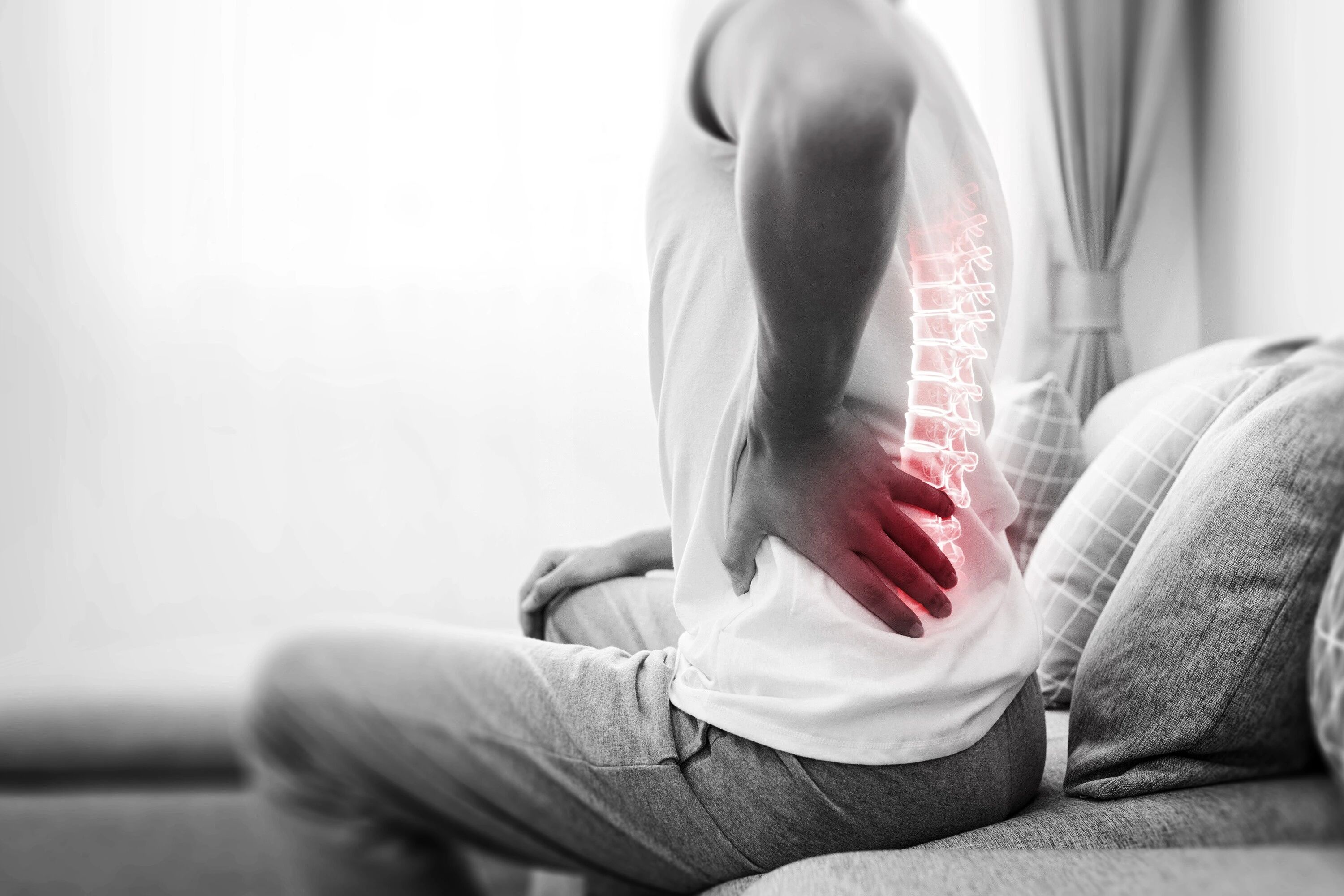
Bone and joint degeneration begins as early as age 30.
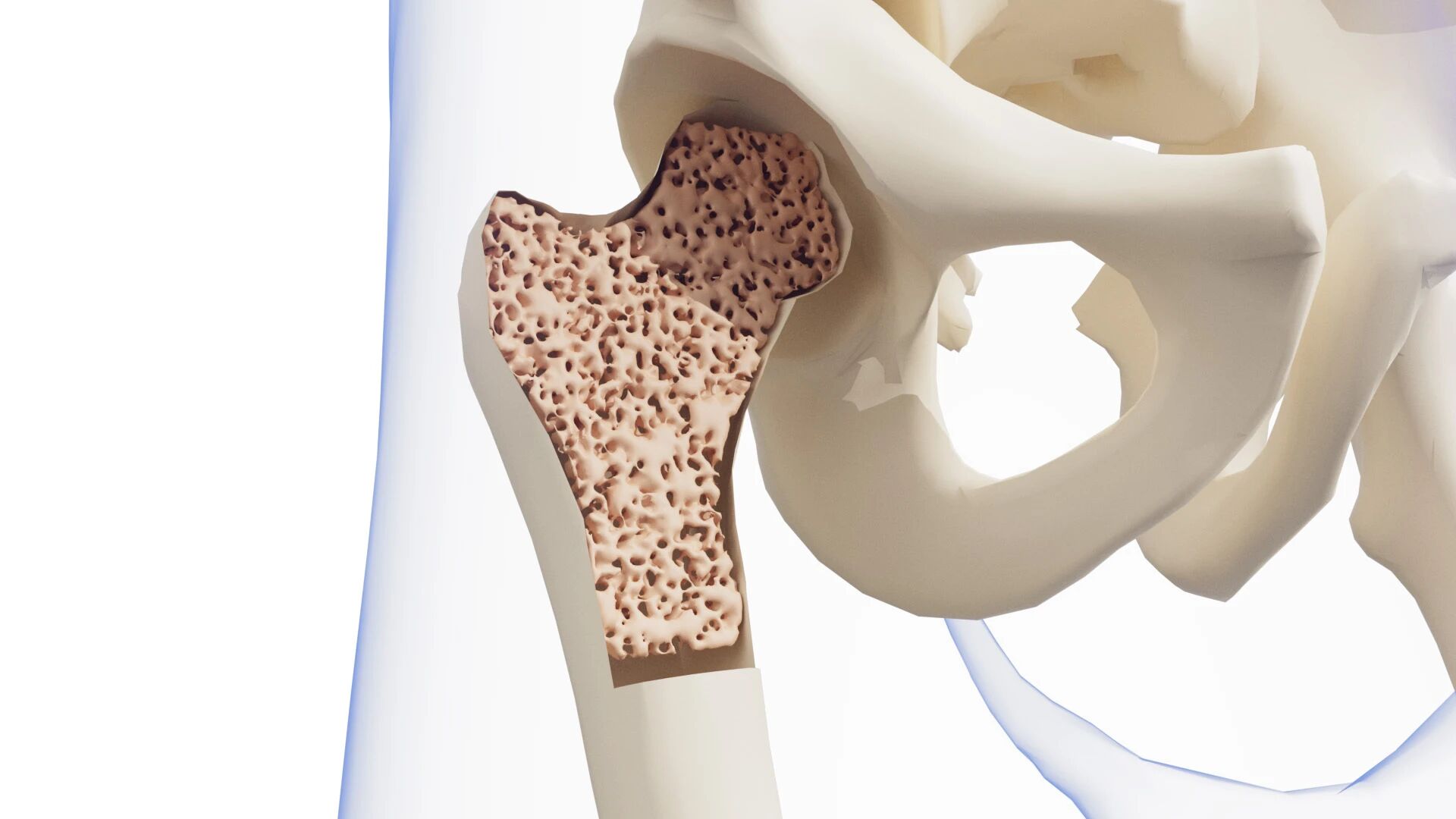
Starting at age 30, the rate of bone formation gradually slows down compared to bone loss. After age 60, bone loss accelerates significantly, leading to decreased bone strength and increased fragility, causing osteoporosis. Approximately 20% of these patients will experience fractures. For the elderly, fractures can lead to complications such as bedsores, pneumonia, and lower limb thrombosis, which can potentially be fatal.
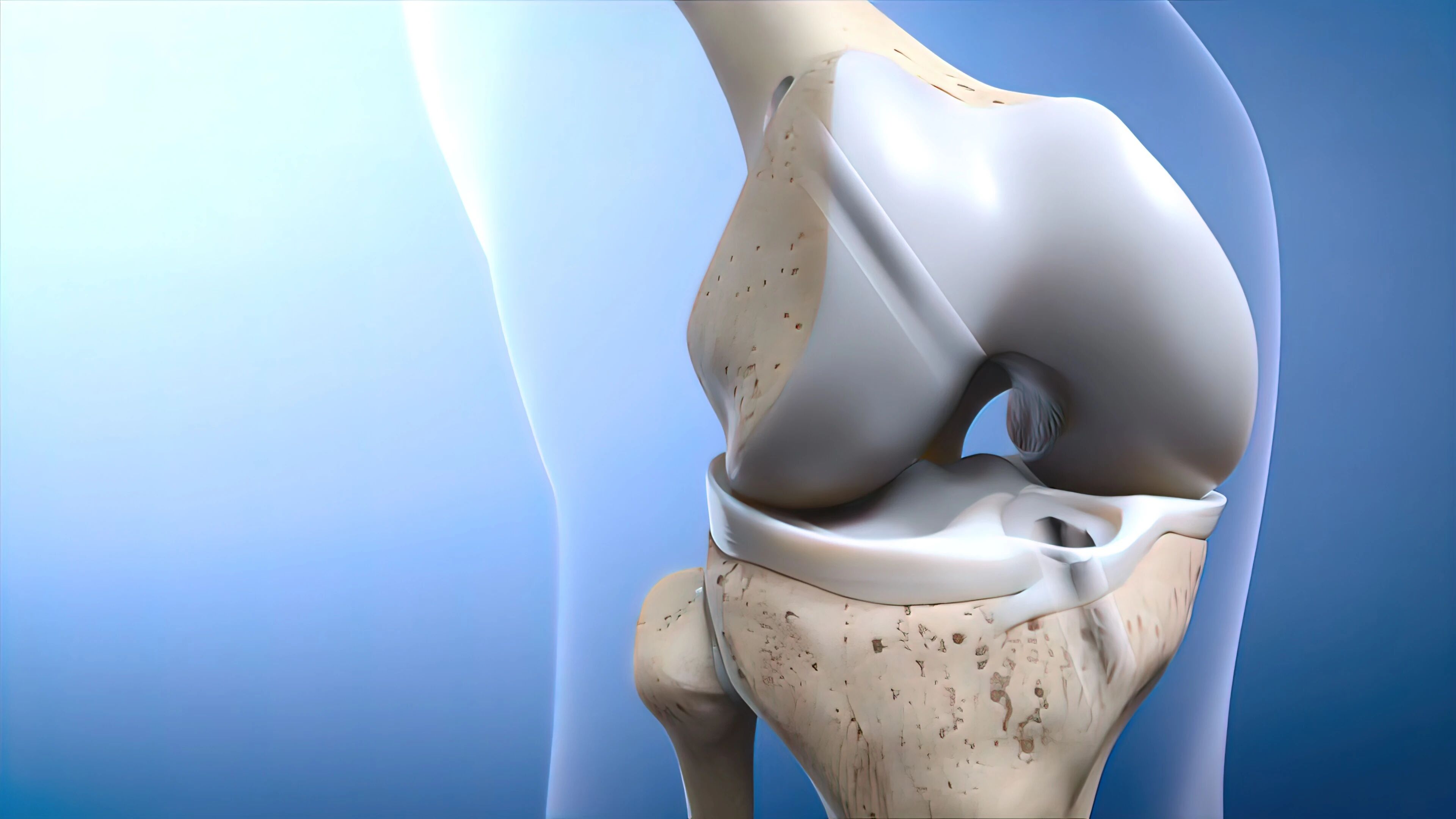
Joint degeneration also begins around age 30. Wear and tear on articular cartilage and meniscus can cause mild joint pain. Excessive weight and improper exercise can accelerate this process, eventually leading to osteoarthritis, which can cause joint pain, stiffness, swelling, limited mobility, and deformities, severely affecting daily life.
Three major protective effects of peptides on bones
Collagen peptides are mainly extracted from terrestrial and aquatic animals. Bovine bones, yak bones, deep-sea cod, sea cucumbers, and jellyfish are all high-quality sources of collagen peptides, which play an important role in promoting bone health.
01 Strengthen bones and prevent bone loss
Bovine bone peptides can effectively prevent the transport of calcium from bones into the blood, increase bone adhesion and trabecular bone hardness, enhance bone toughness, and have a beneficial effect on bone metabolism.
Studies have found that collagen peptides extracted from yak bones can act as a growth factor, promoting the differentiation of bone marrow cells into osteoblasts, thereby increasing osteoblasts, improving the relative imbalance between osteoblasts and osteoclasts in middle-aged and elderly people, and keeping bone growth in a benign state.
02. Maintain joint health and relieve pain.
Collagen peptides derived from animal cartilage can increase synovial mucus content, alleviate pain in patients with osteoarthritis, and improve joint flexibility. This effect is attributed to its excellent bioavailability and its stimulating effect on extracellular matrix synthesis.
A human trial investigating knee osteoarthritis symptoms in elderly women showed that, compared to the control group, patients treated with collagen peptides experienced significantly reduced joint pain and stiffness, and improved joint function.
03 Repair cartilage and reduce wear and tear
Studies have confirmed that collagen peptides can inhibit the loss of chondrocytes and the thinning of the articular cartilage layer caused by phosphorus-induced degradation, promote chondrocyte proliferation, and play a protective and repairing role in articular cartilage.
In a study of athletes with cartilage damage, three athletes underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans after receiving comprehensive treatment including collagen peptide supplementation. The results showed that the surfaces of their joints had recovered.
Healthy and strong bones rely on the support of collagen peptides. Related studies have also found that collagen peptides can promote muscle tissue repair and effectively prevent muscle loss. Therefore, daily supplementation with collagen peptides can help slow down the aging of the musculoskeletal system, allowing for greater mobility and reducing the risk of falls and fractures.
References:
[1] Liu Hong. Composition and Diseases of the Human Musculoskeletal System [J]. Health Guide, 2011, 4.
[2] Luo Yongkang. Functions and Preparation of Bioactive Peptides [M]. China Light Industry Press, 2019.
[3] Hong Hui, Tan Yuqing, Luo Yongkang. Functions and Applications of Collagen and Collagen Peptides [M]. China Light Industry Press, 2022.
Article source: Internet, network; This account is a sharing platform. If there is any infringement, please contact us in time and we will delete it immediately.
Post time: Nov-18-2025